前言
Consistent Hashing 算是前陣子在看的一個分布式演算法,在以往採用 Load Balance 的演算法有許多種,像是 Round Robin,HASH,Least Connection,Response Time,Weighted,而 Consistent Hashing 這種方式可以應用在某個經典場景:
舉 Cache 的例子來看,假如你有三個 Node {A, B, C},然後有 { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} 這六筆資料,一般而言我們會很直覺想把他們平均打散在 cache server 上面,所以會採用 % 3 的方式,而資料也會被映射為
A, {1 4}
B, {2 5}
C, {3 6}
但現在問題來了,假如我現在想多增加一個 Node,根據我們之前的演算法將會變成
A, {1 5}
B, {2 6}
C, {3 }
D, {4 }
如果這個時候刪除 B 這個 Node
A, {1 4}
C, {2 5}
D, {3 6}
大家可以發現資料搬移量很大,我們必須要把資料移來移去,而這種情況在資料大的時候,非常不利於 Cache Server 的 Performance。
解決方案 Consistent Hashing
Consistent hashing is a special kind of hashing such that when a hash table is resized and consistent hashing is used, only K/n keys need to be remapped on average, where K is the number of keys, and n is the number of slots.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Consistent_hashing
利用 Consistent Hashing 的概念就是,要減少資料的搬移量,而演算法的概念也很簡單,我們會將 Node & Data 對應到一個0~2^32的環(continuum)上面
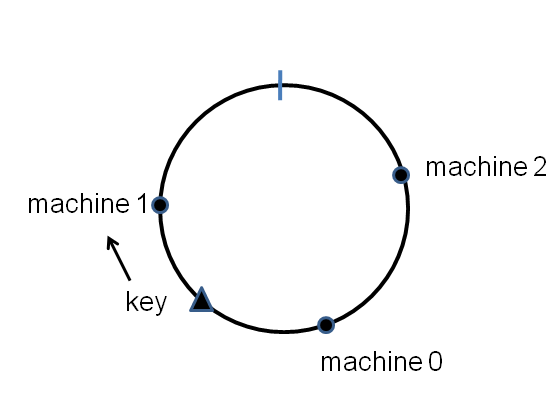
然後透過 Hash function 轉換,然後 Data 會存在順時針方向上面的 Node
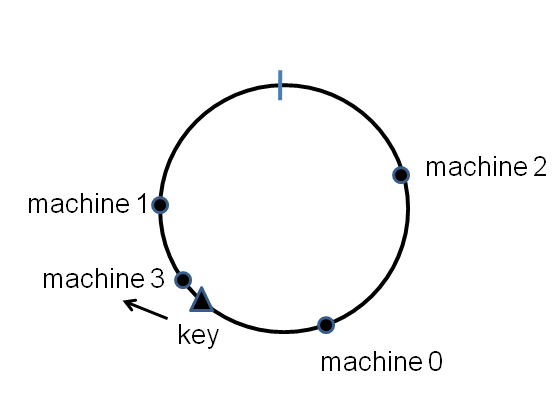
新增節點時,需要 remap Data 到新的 Node 上面
取自「Consistent hashing」這裡
實作
為了更瞭解 Consistent Hashing,這邊有個小小的用 golang 寫的實作。
基本上我先定義出我們的環還有上面的節點
1 | type Ring struct { |
而每一個 Node 上面都有記錄自己的 HashId
1 | func (r *Ring) AddNode(id string) { |
我們在新增節點時,會對 HashId 去做 Sorting ,這樣一來就可以得到一個排列好的 r.Nodes,而在 Golang 裡面要完成 Sort,只需要提供以下介面
1 | // implement sort.Interface |
接著我們在實作 Get ,主要會把 Data 的值通過 Hash 後,找到順時針對應的節點。
1 | func (r *Ring) Get(key string) string { |
虛擬節點
這個演算法真的在實作時,如果 Node 數量太少,其實透過 Hash function 很有可能會 map 到鄰近的位置,導致數據分佈變得極不平均,而就有了虛擬節點這個解法,可以看到下圖,每個 Node 其實都有四個虛擬節點,這樣一來可以更平均的覆蓋這個環
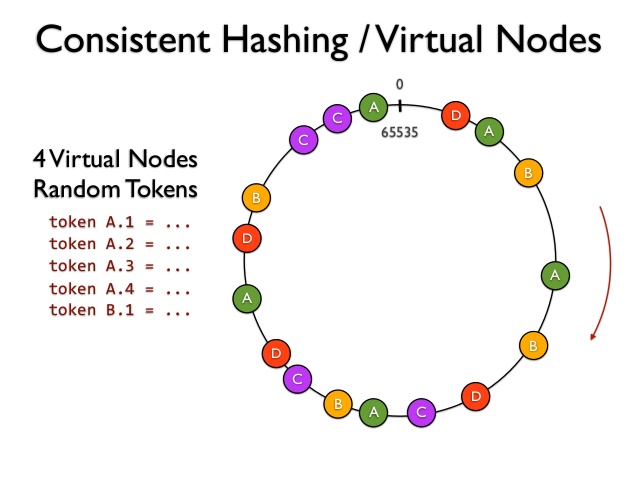
取自「NoSQL Essentials: Cassandra」這裡
結論
Consistent Hashing 盡力地減少 Hash 過的 Data 重新分布,而真正實作上,免不了要利用 Virtual Node 才能達成平均覆蓋環的功用。
另外 gslin 大大提到的 jump-consistent-hash 也很有趣,可以更有效的提升速度和解決平均性的問題,只是那段 Magic Number 實在太妙了,真的要 K 一下 paper 才看得懂。
Reference
Consistent hashing, a guide & Go library
一致性Hash算法(Consistent Hash)
groupcache