Introduction
This post is used to note down how to setup Managed VPN connection between office to AWS by using Mikrotik RouterBoard. We basically follow instructions of this document and it litterally describes everything we need to know. AWS supports Internet Protocol security (IPsec) VPN connections. Following figure shows the architecture of VPN connection.

Components of VPN
Virtual Private Gateway
A virtual private gateway is the VPN concentrator on the Amazon side of the VPN connection. We can specify the Autonomous System Number (ASN) for the Amazon side of the gateway.
Customer Gateway
A customer gateway should be a device or software VPN on our side for VPN connection.
we should define following items
- Internet-routable IP address: Our side public IP address
- The type of routing: static or dynamic
One thing we need to know is that VPN connection is initiated by our side.
AWS Managed VPN
By using AWS managed VPN, we can have several benefits.
- Fully managed by AWS, and AWS also provides HA for us. we no longer need to worry about VPN disconnection issues while zone down.
- IPSec site-to-site tunnel with AES-256, SHA-2.
Our Settings
In this article, we will try to use BGP routing connecting with AWS managed VPN.
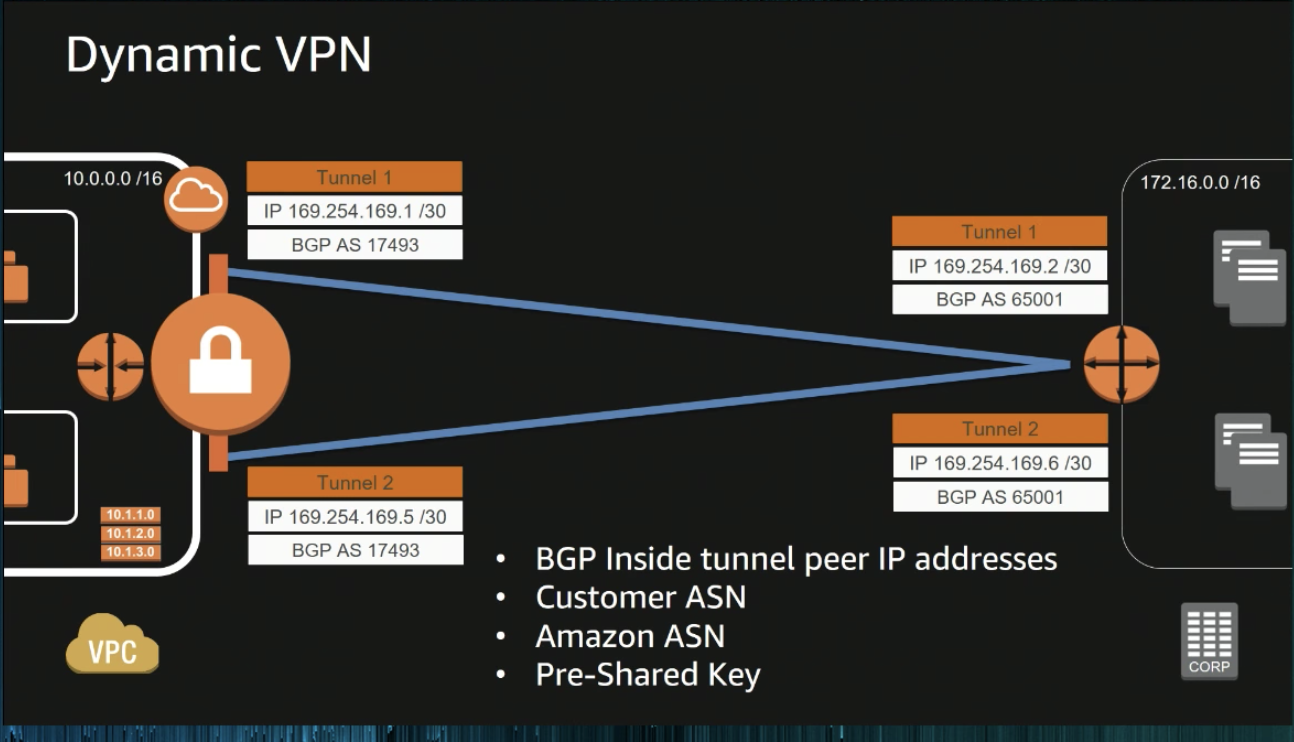
In AWS side:
- Open the Amazon VPC console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/vpc/.
- Choose Virtual Private Gateways, Create Virtual Private Gateway and create a virtual private gateway.
- attach VPC that you wanna connect to
- Create a Customer Gateway
- choose VPN Connections, Create VPN Connection.
- specify Virtual Private Gateway and Customer Gateway
- Routing Options → BGP
- Route Tables → Route Propagation
In Customer Network:
- Download configuration file from AWS VPN connections:
- vendor: Mitrotik
- Platform: RouterOS
- Software: 6.36
- Download routerboard script generator from https://github.com/kkc/aws-vpn-mikrotik
- Run script by using ./dynamic-router-config vpn-94e3fff5.txt
- Performing script mikrotik-aws-config at routerboard
Example of routerboard config1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58# tunnel1 & tunnel2 CIDR
/ip addr
add address=169.254.47.58/30 interface=ether1-WAN
add address=169.254.46.146/30 interface=ether1-WAN
# ipsec proposal
/ip ipsec proposal
add auth-algorithms=sha1 comment="AWS PROPOSAL" enc-algorithms=aes-128-cbc lifetime=1h name=aws pfs-group=modp1024
# ipsec policy
/ip ipsec policy
add src-address=0.0.0.0/0 src-port=any dst-address=10.0.0.0/16 dst-port=any protocol=all action=encrypt level=require ipsec-protocols=esp tunnel=yes sa-src-address=$YOUR_OFFICE_PUBLIC_IP sa-dst-address=$TUNNEL1_IP proposal=aws priority=0
add src-address=0.0.0.0/0 src-port=any dst-address=10.0.0.0/16 dst-port=any protocol=all action=encrypt level=require ipsec-protocols=esp tunnel=yes sa-src-address=$YOUR_OFFICE_PUBLIC_IP sa-dst-address=$TUNNEL2_IP proposal=aws priority=0
add src-address=0.0.0.0/0 src-port=any dst-address=169.254.47.57/32 dst-port=any protocol=all action=encrypt level=require ipsec-protocols=esp tunnel=yes sa-src-address=$YOUR_OFFICE_PUBLIC_IP sa-dst-address=$TUNNEL1_IP proposal=aws priority=0
add src-address=0.0.0.0/0 src-port=any dst-address=169.254.46.145/32 dst-port=any protocol=all action=encrypt level=require ipsec-protocols=esp tunnel=yes sa-src-address=$YOUR_OFFICE_PUBLIC_IP sa-dst-address=$TUNNEL2_IP proposal=aws priority=0
/ip ipsec peer
add address=$TUNNEL1_IP/32 local-address=$YOUR_OFFICE_PUBLIC_IP passive=no port=500 auth-method=pre-shared-key secret=$YOUR_SECRET generate-policy=no exchange-mode=main send-initial-contact=yes nat-traversal=no proposal-check=obey hash-algorithm=sha1 enc-algorithm=aes-128 dh-group=modp1024 lifetime=8h lifebytes=0 dpd-interval=10s dpd-maximum-failures=3
add address=$TUNNEL2_IP/32 local-address=$YOUR_OFFICE_PUBLIC_IP passive=no port=500 auth-method=pre-shared-key secret=$YOUR_SECRET generate-policy=no exchange-mode=main send-initial-contact=yes nat-traversal=no proposal-check=obey hash-algorithm=sha1 enc-algorithm=aes-128 dh-group=modp1024 lifetime=8h lifebytes=0 dpd-interval=10s dpd-maximum-failures=3
# firewall rules
/ip firewall filter
add chain=input action=accept protocol=ipsec-esp src-address=$TUNNEL1_IP dst-address=$YOUR_OFFICE_PUBLIC_IP in-interface=ether1-WAN place-before=1
add chain=input action=accept protocol=udp src-address=$TUNNEL1_IP dst-address=$YOUR_OFFICE_PUBLIC_IP in-interface=ether1-WAN src-port=500 dst-port=500 place-before=1
add chain=input action=accept protocol=ipsec-esp src-address=$TUNNEL2_IP dst-address=$YOUR_OFFICE_PUBLIC_IP in-interface=ether1-WAN place-before=1
add chain=input action=accept protocol=udp src-address=$TUNNEL2_IP dst-address=$YOUR_OFFICE_PUBLIC_IP in-interface=ether1-WAN src-port=500 dst-port=500 place-before=1
add chain=input action=accept protocol=tcp src-address=169.254.47.57 dst-address=169.254.47.58 dst-port=179 place-before=1
add chain=input action=accept protocol=tcp src-address=169.254.46.145 dst-address=169.254.46.146 dst-port=179 place-before=1
add chain=forward action=accept src-address=10.0.0.0/16 in-interface=ether1-WAN
add chain=forward action=accept dst-address=10.0.0.0/16 in-interface=ether2-master
# nat rule
# critically important to AWS connectivity that this rule be ahead of "masquerade".
/ip firewall nat
add comment=AWS-VPN chain=srcnat action=src-nat to-addresses=192.168.0.0/24 dst-address=10.0.0.0/16 place-before=0
add comment=AWS-VPN chain=dstnat action=accept src-address=10.0.0.0/16 in-interface=ether1-WAN place-before=0
/routing bgp instance
set default disabled=yes
add as=65101 client-to-client-reflection=no name=vgw-1 redistribute-static=yes router-id=169.254.47.58
add as=65101 client-to-client-reflection=no name=vgw-2 redistribute-static=yes router-id=169.254.46.146
/routing bgp network
add network=192.168.0.0/24
/routing bgp peer
add hold-time=30s instance=vgw-1 name=a
Troubleshooting
If the connection doesn’t work due to some reason, we can try following troubleshooting step.
Verify interesting traffic
- ESP => allow IP protocal 50 open
- IPSEC Phase2 => Verify encryption parameter AES-128 and hashing parameter SHA-1
- IPSEC PHase2 => Lifetime is configured to 3600s or 1hour
- Ensure that perfect forward (PFS) is enabled
- Verify port 500 is not blocked
Reference
- AWS re:Invent 2017: Deep Dive: AWS Direct Connect and VPNs (NET403)
- Create IPSec VPN connection between AWS VPC and customer network
- How do I troubleshoot phase 1 IKE issues with an AWS VPN connection
- How do I troubleshoot phase 2 IKE issues with an AWS VPN connection